
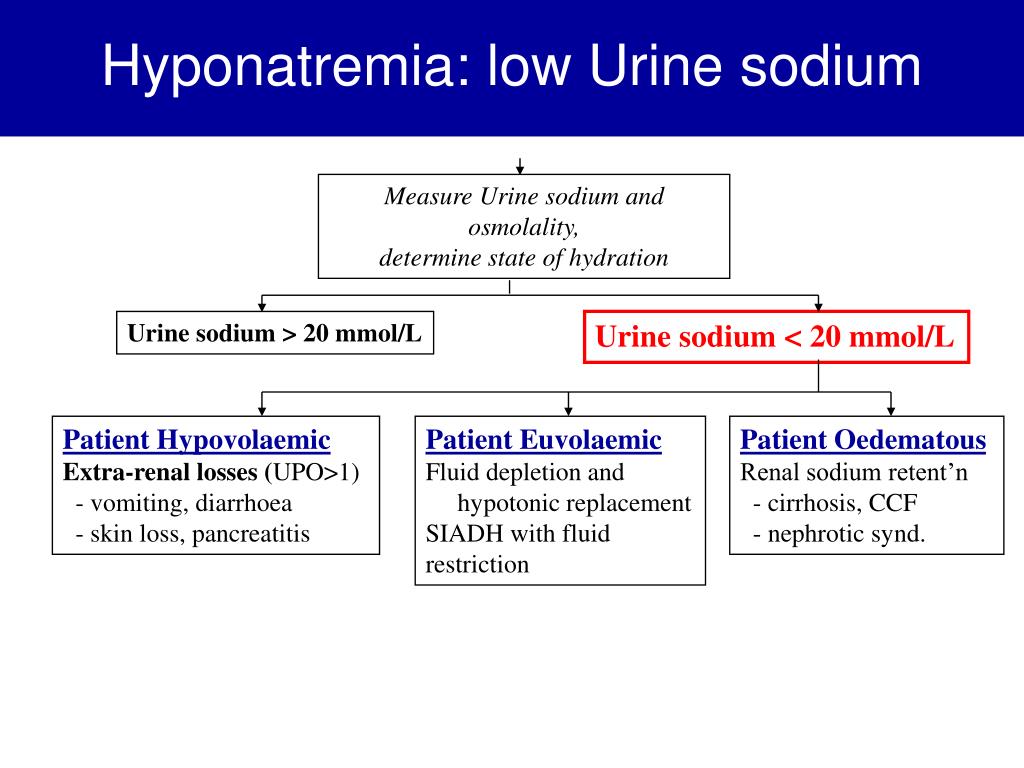
Just under 30 % is contained in a non-exchangeable state in bones. The adult human body contains around 3500 mmol (80 g) of sodium. However, with a brief overview of normal sodium metabolism and Published case histories, the danger of failing to recognize Pseudohyponatremia will be discussed, and with the help of two Indicators that help establish a diagnosis of Purpose of this article is to outline how some laboratory methodsĬan, in certain well-defined clinical situations, give rise to aįalsely low plasma sodium concentration, and thereby a diagnosis of Not true hyponatremia but so-called "pseudo"hyponatremia. Rare possibility that the result is spuriously low: that this is Of the hyponatremic patient should include due consideration of the Plasma sodium depends on establishing the cause. Hyponatremia (reduction in plasma sodium) is diagnosed if the Of the most frequently requested blood tests in clinical practice.Īlthough usually performed in the laboratory, the test is alsoĪvailable at the point of care using technology incorporated intoīlood gas and other point-of-care analyzers.Ĭoncentration is maintained between 135 and 145 mmol/L, so that Sodium levels in urine will be high.Measurement of plasma/serum sodium concentration is one Sodium loss due to kidney diseases, Addison's disease or administration of diuretic medication.There are some diseases associated with hypernatremia like Cushing's syndrome or diabetes insipidus.Ībnormally low levels of sodium in the blood ( hyponatremia) may be due to: High sodium level in the blood ( hypernatremia) may be due to dehydration. It helps also to evaluate the hormones involved in the sodium balance and estimate the hydration state of the body. It is usually performed along with the study of sodium in urine to get more information. ADH hormone promotes water retention in the kidneys.Ī sodium blood test can be useful to determine your kidney function. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): Produced by posterior pituitary.Natriuretic hormone: Produced by the heart, natriuretic hormone promotes sodium and water excretion in the urine.Aldosterone: Produced by the adrenal gland, aldosterone increases sodium and water retention in the kidneys.Three major hormones are involved in regulating sodium and water balance in the body:

When the sodium level in the blood is low, kidneys get rid of excess water by urine.When the sodium level in the blood is high kidneys conserve water.A little part can be excreted also through stools or sweat. Sodium is excreted primarily in urine by the kidneys. Sodium is found in salt (sodium chloride). Thus, sodium is a key substance to regulate osmolality. That way, if there is an increase in the solutes (dissolved particles) outside the cells that pulls the water out of the cells and vice versa. The total concentration of these substances (osmolality) inside and outside the cells must be the same. Sodium, potassium, proteins and other soluble substances are dissolved in it. Water can be found inside the cells (two-thirds) or outside the cells (one-third). Sodium is the main electrolyte in the bodily fluids (urine, blood, stools) and its role along with potassium, chloride and CO2 (bicarbonate) is essential to maintain electrical neutrality in the cells and the acid-base balance. Plasma osmolality measures primarily the amount of dissolved sodium in the serum (blood). Osmolality measures the electrolyte-water balance of the body. Sodium plays an important role in maintaining a correct osmolality. Sodium is an electrolyte found mainly in the extracellular fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
